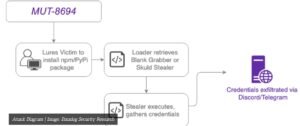
The open-source ecosystem has once again become the battleground for cybercriminals, as Datadog’s Security Research team uncovered a coordinated supply chain attack by an enigmatic threat actor designated MUT-8694. Leveraging malicious npm and PyPI packages, the actor has launched an extensive campaign aimed at infiltrating developers’ environments, predominantly targeting Windows users.
On October 10, 2024, Datadog’s CLI tool, GuardDog, detected a malicious PyPI package named larpexodus. The package included a PowerShell command that downloaded and executed a Windows binary hosted on GitHub, later identified as the Blank Grabber infostealer. Datadog noted: “The malicious packages on both npm and PyPI masquerade as legitimate packages, often through the use of typosquatting.”
These packages exploit common developer mistakes, such as typing errors, to deliver obfuscated malware. In the npm ecosystem, for example, the nodelogic package was found using post-installation hooks to execute malicious JavaScript that retrieved similar infostealer payloads.
MUT-8694’s campaign predominantly employs two types of malware:
- Blank Grabber
Compiled from an open-source project, Blank Grabber is a versatile infostealer targeting:- Roblox cookies
- Cryptocurrency wallets
- Browser passwords
- Telegram sessions
It also disables Windows Defender through advanced PowerShell commands, ensuring persistence and stealth. Datadog remarked: “The malware has some evasion capabilities, along with stealer code that targets Roblox cookies, crypto wallets, browser passwords, Telegram sessions, and more.”
- Skuld Stealer
Written in Go, this malware focuses on Discord users and employs robust evasion techniques such as virtual machine detection, token theft, and browser credential extraction. Skuld Stealer ensures persistence by copying the binary to the Windows startup directory and disguising itself as a legitimate service.
Datadog’s analysis revealed 42 malicious PyPI packages and 18 npm packages linked to the campaign, each mimicking legitimate libraries. The PyPI packages falsely claimed to resolve DLL and API issues, while many npm packages referenced Roblox development, suggesting a specific focus on targeting that community.
The threat actor utilized GitHub and repl.it to host malicious payloads, exploiting these legitimate platforms to evade detection. “The repeated use of obfuscation and the employment of publicly available infostealers… illustrate the adaptability and persistence of this threat actor,” Datadog warns.
(source: securityonline.info)



